Since the inception of the administration of Ogbeni Rauf Aregbesola as the Governor of Osun State on Saturday, November 27, 2010, after lengthy rounds of litigation to reclaim his stolen mandate, the governor has left no one in doubt about his intention to develop the state as quickly as possible.
Even in the face of lean resources, Aregbesola’s passion to transform Osun into a state where government worked for the people remained unwavering. The results can be seen in the far-reaching impact of government activity and investments in key sectors of the economy today.
The shape of things to come were made clears as far back as 2005, with the establishment of the Oranmiyan Foundation, a political platform, by Governor Aregbesola and the launch of the Green Book that contained the planned programmes of the then Lagos State Commissioner for Works.

The book outlined his planned policies and programmes and as the April 14, 2007 governorship poll moved closer, many residents of state had become so familiar with the sixpoint integral action plan of Aregbesola.
The Six-point Integral Action Plan as expounds in the Green Book that the governor himself had described as the document of trust and symbol of contract with the people of Osun State are : Banish hunger, banish poverty, banish unemployment, promote healthy living, promote functional education, promote communal, peace and progress. These six points are defined as integral because the delivery of the development vision, according to the governor requires a combined implementation of each of these points.
With barely six months to the end of the first four year tenure of Ogbeni Rauf Aregbesola, the impact of government is being felt in every part of the state with basic infrastructural amenities being put in proper shape.

Banish hunger, banish poverty, banish unemployment
In tandem with the first three items on the six point integral action plan, the administration of Ogbeni Rauf Aregbesola, within 100 days in office employed 20,000 youths under a programme called Osun Youth Empowerment Scheme, OYES, setting the record as the first government in the history of the country to absorb such number of unemployed youths at a time.
The youths, who were subjected to training in specific areas of needs, upon completion of their induction exercise were immediately deployed to relevant sectors such as traffic management, health, sanitation, works and security. The youths, who had their uniforms sown by the designers selected from the state, were placed on the monthly stipend on N10,000 and the first batch of cadets captured under the programme had already completed their assignment and another set recruited.
The youth empowerment programme, which was recommended by World Bank as a model to the Federal Government and also being adopted by some state governments across the country, has successfully created a new category to spenders through whom an additional N200m is being injected into the economy of the state monthly.

Apart from OYES scheme, the administration of Aregbesola has also empowered other categories of people in the state by engaging them through mutually beneficial ventures. The present administration has also entered the history books as the only government till date that will employ the highest number of civil servants despite executing several capital intensive projects.
The vacuum created by the mass retirement from the service of Osun State Government in 2012 occasioned by the introduction of contributory pension scheme, which left the state work force badly depleted, were quickly plugged with the recruitment of workers into the civil service.
Similarly, the Aregbesola administration also recruited qualified teachers, who were made to pass through various stages of screening, with priority attention to the core subjects like English and Mathematics, among others to improve the quality of instruction being provided in public schools across the state.
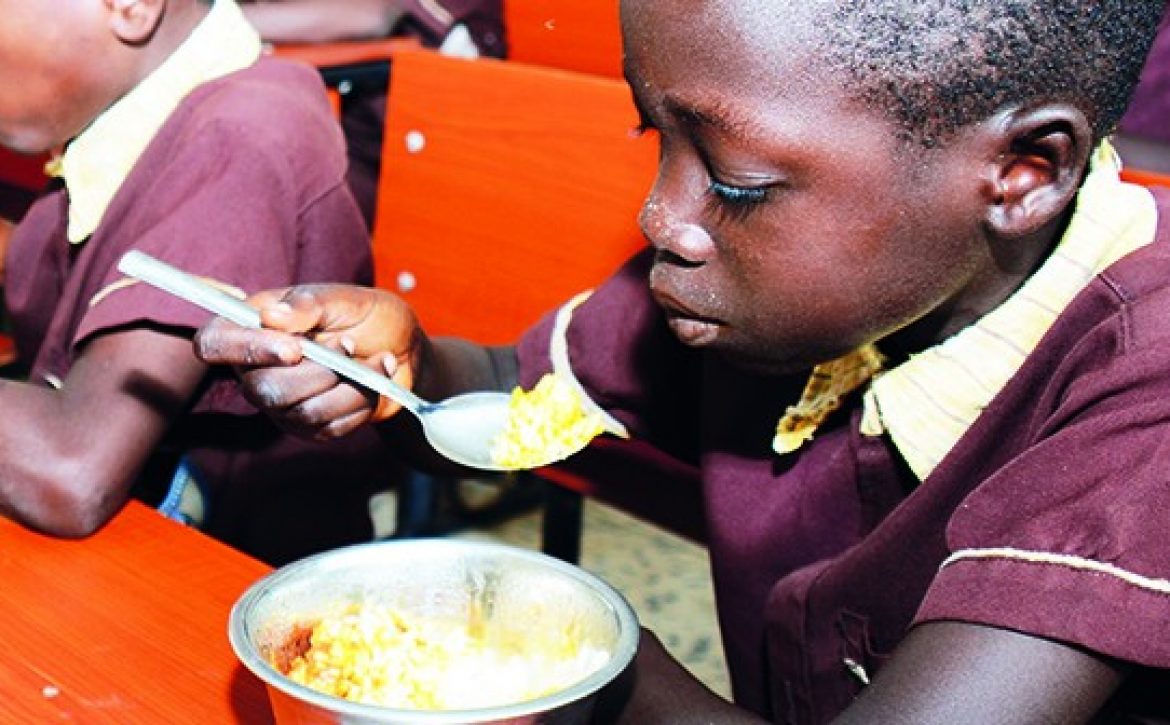
The government also created jobs through programme such as the reinvigorated school feeding programme tagged “OMeal, through which about 250,000 pupils in public schools are being fed once in a day. The cooks that prepare the food are another group of new spenders created by Osun State Government.
Another programme created to take care of unemployed persons and the vulnerable is Agba Osun initiative through which the aged in the state are given a monthly stipend of N5,000.

Promotion of healthy living
In its bid to promote healthy living among the people of Osun State, Aregbesola, himself a fitness buff, declared an emergency in the area of sanitation on assumption of office in 2010 and with the collaboration of health officers attached to all the local government areas in the state began a more careful supervision of cleaning of streets, business premises and residential buildings by health workers while ad hoc staff were recruited and the filth that had taken over major streets of the capital under the previous administration, quickly disappeared.

At the expiration of the emergency programme, another scheme designed to sustain the gains achieved tagged O’Clean Plus was introduced. Under this program, over 100 refuse vans were bought and towns with in the state were assigned to different private refuse disposal companies, who turn up once in a week to remove refuse while people pay for the services they render.
Also, this administration is proactive in the aspect of flood prevention led to the dredging of over 123 kilometres of streams, rivers and canals throughout the state. It was a preventive action taken by the government after repeated warnings of severe flooding nationwide by meteorological agencies.
Osun has been one of the flood free states during the turbulent massive rainfall and change in weather conditions in the last few years. Flood prevention has been a constant activity embarked upon by the state even before the red signal of the weather agencies. Several lives and valuable properties have been saved through this proactive step.

Presently, nine general hospitals spread across the nine Federal Constituencies in the state are being simultaneously renovated at the whooping sum of N2bn. The renovation works which are at different stages of completion include upgrade of medical equipment and facilities.
Also, the state Ministry of Health, as part of measures to ensure healthy living among people of the state, has been organising free surgeries for people, who could not afford it in each of the nine biggest cities in the state where surgeries were performed free on people suffering from hernia. Similarly, the ministry has also organised free eye surgeries for people in Osogbo, the state capital and also provided, if situation demands, post-operation services for their patients.

Promotion of functional education
It is on record that the present administration has initiated some of the most ambitious programmes and policies to revamp the education sector.
Through its reclassification programme, Aregbesola’s administration re-arranged public primary and secondary schools in the state into elementary, middle and high schools and merged already existing schools to form new mega schools with modern facilities.

In the new policy, elementary level comprises of pupils from ages six to nine years, which corresponds to primary one to four pupils under the existing system. The middle level is from primary four to JSS 3 of ages 10 to 14, now classified as grades 5-9, and the high school level age range are between 15 and 17 years, corresponding to Senior Secondary School III, to be known as grades 10- 12.

The committee for the implementation of O’ School headed by Chief Layi Oyeduntan, during the foundation laying ceremony of the first mega school that was built under the programme in Ejigbo, said 100 elementary schools, 50 middle schools and 20 high schools would be built across the state.
Less than two years after, the committee has succeeded in completing nearly all the proposed schools and those already completed are presently being occupied by students. The schools, designed to reflect the basic global standard for modern schools, have all the necessary facilities that makes academic activities conducive.

The Osun Elementary School Feeding and Health Programme now known as O-Meals is one of the few surviving school meal programmes in the country. It was formerly known as the Home Grown School Feeding and Health Programme. This has now been restructured and enhanced by the present administration to reach a larger number of students (254,000) and to empower over 3,000 community caterers. The revamped programme has helped increase school enrolment by a minimum of 25 per cent.

The Osun State Government is also providing 150,000 e-learning tablets, known as Opon Imo, for Senior Secondary School student. This initiative, the first of its kind anywhere in the world, covers 17 core subjects with over five extra curricula subjects for Senior Secondary 1, 2 and 3 levels. The tablets contain over 56 textbooks , 900 minutes of virtual classroom lessons and thousands of Practice Play ground of Ilare Elementary school, Ile-Ife Questions for WAEC and JAMB. In addition to aiding preparation for School Leaving Examinations, the introduction of the tool is expected to aid adoption of information communication technology (ICT) skills among students in the State.

Agriculture
A number of incentives have been given by the present administration to boost agricultural production in the state.

These include support to 220 farmer groups under the Osun Broiler Outgrower Scheme (OBOPS), 28 cooperative groups have been empowered to plant 17 hectres of maize, 500 acres vegetable cluster, while 2,000 farmers have also been supported to plant 1.3 million plantain suckers for refined plantain production. In all, a total of 10,698 acres of farmland have been cultivated with the support of the Government of the State of Osun.
Also, 1,830 rural farmers in 61 focal communities have been equipped with farm inputs under the UNICEF replication initiative programme of the Ministry of Water Resources, Rural and Community Development.
Considerable attention is being paid to rural and community development under the UNICEF Community Development Replication Initiative Programme of the Ministry of Water Resources.
Similarly, a total of 122 boreholes have been sunk in the focal communities. The UNICEF Replication Programme is a three year rolling scheme focusing on two communities per local government for development interventions.

Security
The Osun State Government, apart from providing about 125 patrol vehicles to security agencies such as the Army, Police, FRSC, NDLEA and the Civil Defence, also bought five armoured personnel carrier, the first in the history of the state to fight incessant robbery attacks. It is also noteworthy that the helicopter acquired was for area surveillance and ‘’quick emergency response’’ in the state. Since this noble initiative, crime, especially bank robberies has reduced significantly to the barest minimum.

Works and infrastructure
The government of Ogbeni Rauf Aregbesola has unbelievably raised the bar of governance in terms of roads and infrastructural amenities development generally. The present administration has constructed close to one thousand kilometres of roads of both intra-city and intercity status, expending over N10bn on projects
The governor recently commissioned over 21 kilometres Ilesa township roads, while other newly roads in other cities in the state, it was learnt will soon be commissioned.
Osogbo, the capital of Osun state has enjoyed the privilege of having lion’s share of the township roads constructed. Recently, the state governor commissioned 21 newly constructed township roads within the state capital stretching 26.31 kilometres.
The selected roads under the first phase constructed and rehabilitated in the last 3 ½ years targets constructing roads with a life span of between 15-20 years. It features drainage construction fortified with iron and concrete thickness of between 60mm-70mm, a departure from using blocks which cannot stand the test of time. The drainages have been constructed to ensure smooth flow of water and also help in controlling erosion activities from washing away the layers of the roads. Aside from fortified concrete drainages, the roads have various layers such as laterite, stonebase and asphaltic overlay of 50mm. The asphaltic thicknesses of the roads are the same all since it is plied by all grades of vehicles.
A unique feature of Ogbeni Aregbesola’s road construction efforts is compliance with the state capital road master plan. The master plan consists of several roads connecting the inner Ring Road and the Outer Ring Road. No administration before now had paid special attention to radically connecting these roads together. The Osogbo Inner Ring Road as constructed by this administration takes off from Off Osogbo-Gbongan Road and routes from Gbodofon-Jaleyemi- Gbemu Junction Road-Isale Aro (1.79km). It leaps over the Oja-Oba Road to connect Gbemu Junction-Oluode Market-Elelede Junction-Abaku Road-Boorepo (1.47km) bursting out and connecting the on-going dualisation of Osogbo-Ikirun-Ila Odo-Kwara State Boundary Road.
The other stretch leaps over the Osogbo-Ikirun-Ila Odo Kwara State Boundary Road and picks off from Church Street-Bisi Bankole/Anaye Market Street- Alaafia Street-Oke Onitea Road- Anaye Market Junction-Oke Onitea Road (2.08km) to connect the existing West By Pass. This forms a semi circle inside Osogbo.
The next stretch is from GRA Road-Adesina Crescent-Ilobu Road (1.35km) and connecting the Osogbo-Ilobu Road. It picks off from Off Osogbo-Ilobu Road from Lameco Junction and routes Oroki Lane( dualised and connects West By Pass at Jerry Paul Filling Station)- Tinumola/ Wonderful Road( opposite Capital Hotel (2.06km). It intersects the Iwo Road/Oke fia Road and takes off from Capital Hotel-Alekunwodo- Coca Cola(2.33km) and burst out on the Osogbo-Gbongan Road to complete the Inner Ring Road formation in the Osogbo Road Master Plan.
Other road constructed/ rehabilitated which interconnects other roads includes Station Road- Fagbewesa-Odi OlowoJunction- Ebenezer Hotel (0.61km). Oja Oba-Osun Groove Gate with Road extension (1.02km), Balogun Biiro/ Oke Baale Road( 0.85km), John Mackay-Gbeja Road-Oke Baale with Constain (0.96), Kola Balogun Road Junction-Fiwasaye Olohunosebi Rd( 0.87km). One important stretch of constructed road is the Heritage Hotel Road-Dupe Aina-Odetoyinbo Rd(3.28km) which connects the on going dualisation of the 18km East-West By Pass Road at the Fountain University End. The second axis which connects the East-West Bye Pass (Outer Ring Road) is the Osunbukola/Mercy Land-Ajani Street-Prime Petrol Station (0.98km) to connect the Ofatedo- Ido Osun Road and connect it at the Ebunoluwa School Area
A careful study of the constructed and rehabilitated roads will reveal an interconnectedness of these roads with one another showing a deliberate, conscious, strategic and skilful road infrastructure upgrade of the State Capital. As stated earlier, the roads with asphaltic thickness of 50mm will no doubt last between 15-20 years thus giving the state value for money.
Also in Osogbo, a massive N4.5bin Eastern bye pass named after late Premier of Western region, Oba Adesoji Aderemi, is about 40 per cent completed.
Work is also ongoing on the Gbongan/Akoda dualisation but the flagship of several roads projects being undertaking by Aregbesola’s administration remains Osogbo/Ila-Odo Kwara Boundary road. The 45 kilometre road passes through three local government areas and cost the state close to N20bn.
Another road project worthy of mention is Gbongan/Orile-Owu/ Araromi/ Ogun State boundary road. This particular road provides an alternative route to Lagos State and many commuters from the state and those coming from the North have already started using it, even when construction work is still going on.
The present administration is also pursuing an ambitious programme aimed at creating markets for goods manufactured within the state and those coming from other states. In the last two years, Aregbesola’s administration has initiated construction of three different markets within the state capital.
Ayegbaju, Aje and Dagbolu regional markets all located within the state capital are simultaneously being constructed by government using public private partnership model. The state Commissioner for Commerce, Mr. Ismaila Alagbada, while speaking to newsmen recently said the first set of shops at Ayegbaju market will be ready for use by June this year.
The dream of having an airport in the state is gradually being brought to fruition with the massive investment of Aregbesola administration on the MKO Abiola Cargo Airport, Ido-Osun.
Slava Yeditepe, an Aeronautical Engineering and Technical Services, the company handling the project, through its supervisor in charge, Abubakar Abuyaro while speaking with newsmen recently, said the airport will have the longest runway in the country by the time it is completed.
Apparently, this is just the tip of the iceberg. The Aregbesola administration, which has established itself as an effective manager of men and material resources looks forward to another term where it is set to deliver even more of the dividends of democracy promises the people on inception.
Indeed the people of Osun appear keen on ensuring the continuity is the watchword at the elections scheduled for August.
This is evident in the massive turnout of supporters on the governor’s campaign trail as he moves across the state to restate his commitment to the complete transformation of the State of Osun.
Aregbesola’s message and vision is clear. With prudent management of resources, innovative ideas and emplacement of policies that will attract both local and foreign investors into the state, Osun will be the model state that other needs to follow. As such there will be no need to change a winning team.
NATIONAL MIRROR